The intra-African trade landscape is rapidly evolving, with key nations at the forefront, driving economic growth and contributing to the continent’s push towards self-sufficiency and integration.
The African Trade Report, a flagship publication of the African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank), has long served as a critical resource on African trade matters.
As Afreximbank expands its influence to the Caribbean and the broader African Diaspora, the report will increasingly adopt a global perspective while maintaining its focus on the continent.
This Global Africa approach aims to build a united and interconnected African economy through enhanced trade and investment, benefiting Africans worldwide.
The 2024 African Trade Report, titled “Climate Implications of the AfCFTA Implementation,” highlights the severe impact of climate change on African economies, noting that climate disasters have already compromised a significant portion of the continent’s trade.
As Africa moves forward with initiatives like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), the leading nations in intra-African trade will play crucial roles in shaping the continent’s economic future, fostering collaboration and enhancing resilience against global economic challenges.
Professor Benedict O. Oramah, President and Chairman of the Board of Directors of the African Export-Import Bank Cairo, Egypt, said, “The AfCFTA is a powerful tool for mitigating carbon emissions and climate change, promoting sustainable economic development, and enhancing industrial transformation across the continent.”
The report highlighted that “In 2023, the value of intra-African trade increased to US$192.2 billion, marking a 3.2 per cent growth compared with the impressive growth rate of 10.9 per cent in 2022.”
“Despite the backdrop of global growth deceleration and macro challenges faced by several nations, intra-African trade demonstrated remarkable resilience. Its share of total African trade reached 14.9 per cent in 2023, an improvement over the 13.6 per cent achieved in 2022. This uptrend reflects the concerted efforts across the continent, including the ongoing implementation of the AfCFTA, aimed at bolstering intra-African trade.” the report reads.
The report further reveals significant regional disparities in intra-African trade. Southern Africa, with a remarkable 41.1% growth in trade with neighbouring countries, will be the top contributor to intra-African trade in 2023.
West Africa maintained its position as the second-largest trading subregion, accounting for 25.7% of the total. East Africa followed as the third-largest, contributing 14.1%. Meanwhile, North and Central Africa accounted for 12.4% and 6.6% of total intra-African trade, respectively.
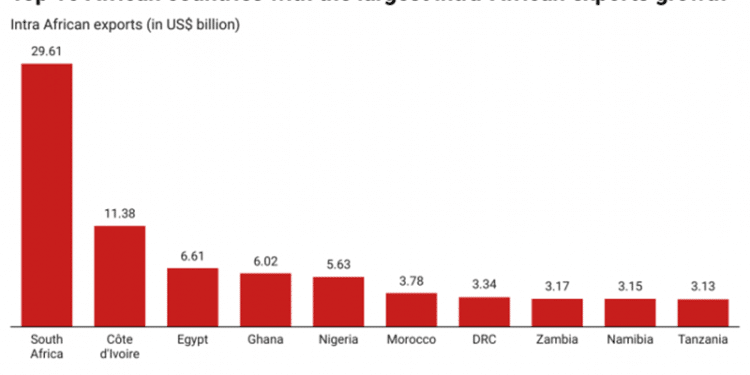
Top 10 African countries with the largest intra-African exports growth in 2023
1. South Africa – South Africa leads the continent in intra-African trade, with exports valued at $29.61 billion, accounting for 26.83% of the total intra-African exports. Although the country experienced a slight decline in growth at -1.34%, its diversified economy, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and developed infrastructure have established it as a central hub for trade within Africa. South Africa’s primary exports, including automobiles, minerals, and machinery, continue to be in high demand across the continent, reinforcing its dominant position.
2. Côte d’Ivoire – Côte d’Ivoire has emerged as a significant player in West African trade, with intra-African exports reaching $11.38 billion, representing 10.31% of the total. Due to its robust agricultural sector, the nation has experienced a remarkable growth rate of 26.40%. Cocoa, coffee, and cashew nuts are among Côte d’Ivoire’s key exports, and the nation’s strategic investments in infrastructure have further bolstered its trade relationships within the continent.
3. Egypt – Egypt, with intra-African exports totalling $6.61 billion, accounts for 5.99% of the continent’s total exports. The country has achieved an 18.69% growth rate, leveraging its strategic location and diversified economy. Egypt’s exports, which include chemicals, agricultural products, and textiles, benefit from the country’s proximity to key trade routes like the Suez Canal, enhancing its role as a gateway for trade between Africa and other regions.
4. Ghana – Ghana is one of Africa’s fastest-growing economies, with intra-African exports valued at $6.02 billion, contributing 5.46% to the continent’s total. Due to its exports of gold, cocoa, and petroleum products, the nation has experienced a significant growth rate of 27.23%. Ghana’s stable political environment and ongoing economic reforms have further solidified its position as a vital trade partner within Africa.
5. Nigeria – Nigeria, Africa’s most populous nation, plays a crucial role in intra-African trade, with exports amounting to $5.63 billion, representing 5.10% of the total. Due to its sizable oil reserves and position as one of the continent’s largest economies, the nation has experienced moderate growth of 8.18%. Nigeria’s key exports, including crude oil, agricultural products, and cement, continue to be essential to its trade relationships within Africa.
6. Morocco – Morocco has steadily increased its intra-African exports to $3.78 billion, accounting for 3.42% of the continent’s total. With a growth rate of 7.39%, the country has focused on sectors such as phosphates, textiles, and automobiles. Morocco’s strategic location and investments in Africa’s infrastructure and banking sectors have helped it become a critical trade hub in North Africa.
7. Democratic Republic of the Congo – The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) remains a key exporter of raw materials within Africa, with intra-African exports totalling $3.34 billion, representing 3.03% of the total. Despite a decline in export growth at -7.79%, the DRC’s economy continues to rely heavily on its rich natural resources, particularly minerals like copper and cobalt. The country faces challenges such as political instability and infrastructure deficits, but it remains an essential trade partner for raw materials in Africa.
8. Zambia – Zambia’s economy is predominantly driven by its copper exports, with intra-African exports reaching $3.17 billion, accounting for 2.87% of the continent’s total. The country has experienced a growth rate of 9.47%, capitalizing on its mineral wealth. However, Zambia continues to face challenges in diversifying its economy to ensure sustainable growth in the future.
9. Namibia – Namibia has shown impressive growth in its intra-African exports, totalling $3.15 billion and representing 2.85% of the total. With a growth rate of 20.22%, Namibia’s exports, which include minerals, meat products, and fish, are vital commodities for neighbouring countries. The country’s commitment to improving its infrastructure and trade policies has positively impacted its trade within Africa.
10. Tanzania – is rapidly emerging as a significant trade player in Africa, with intra-African exports amounting to $3.13 billion, contributing 2.83% to the continent’s total. Due to its diverse economy, which includes manufacturing, mining, and agriculture, the nation has achieved an 18.29% growth rate. Tanzania’s strategic location as a gateway to East Africa further enhances its trade prospects, making it an increasingly important partner in intra-African trade.